
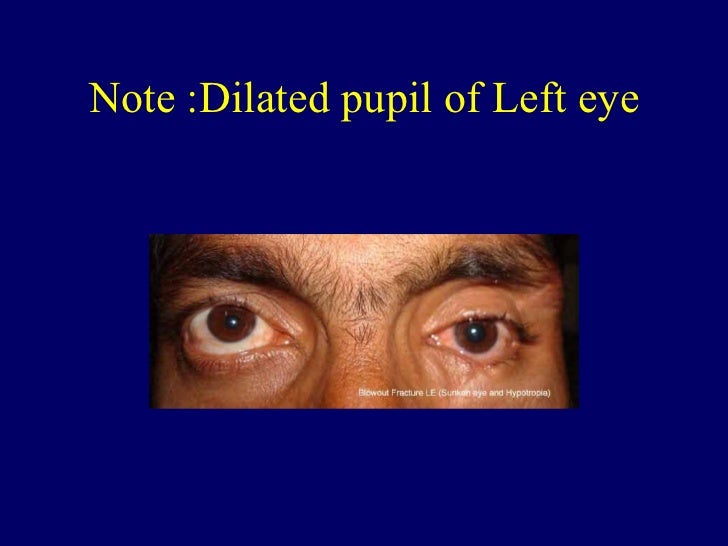
Mydriasis is used as a diagnostic test for Horner's Syndrome, in which it is initiated using a similar mechanism, though cocaine is not usually used in this procedure. Noradrenaline, the neurotransmitter for the SNS, causes dilation of the pupil. When a solution of cocaine is dropped into the eye, noradrenaline is no longer reabsorbed by neurons, and its levels increase. Acetylcholine (ACh) is the neurotransmitter of the parasympathetic nervous system and blocking its action means the pupil cannot constrict.Ĭocaine inhibits the reuptake of noradrenaline (aka norepinephrine) within a nerve synapse. In cases of head or orbit trauma, the iris sphincter (the muscle which is responsible for closing the pupil) or the nerves controlling it can be damaged, reducing or eliminating reactivity to light.Ītropine blocks muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Damage to this nerve typically manifests itself as mydriasis, because the sympathetic supply to the pupil which causes mydriasis remains unaffected, and therefore unopposed. The parasympathetic nervous supply which causes constriction of the pupil, or miosis, is supplied by cranial nerve III, the oculomotor nerve. It usually involves either a disruption of the parasympathetic nerve supply to the eye (which causes contraction of the pupil), or over activity of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS). The mechanism of mydriasis depends on the agent being used. Conversely, parasympathetic stimulation cause contraction of the circular muscle and constriction of the iris. Sympathetic stimulation of α1 adrenergic receptors causes the contraction of the radial muscle, and subsequent dilation of the iris. The former is innervated by the parasympathetic nervous system, the latter by the sympathetic nervous system. There are two types of muscle that control the size of the iris: circular muscle and radial muscle.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
